How does the scheme work?
The scheme covers five of the most important endemic infectious diseases of cattle
The five most important endemic infectious diseases covered by the CHS
- Bovine Viral Diarrhoea (BVD)
- Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
- Johne’s Disease
- Leptospirosis
- Neosporosis
Herd owners may test for most diseases at the same time. Neospora requires females to be tested between 12 and 4 weeks before calving.
Herd owners joining the scheme will pay AFBI a membership fee plus the costs of testing Join the Scheme
Membership includes:
- Veterinary advice on testing, results and biosecurity
- Annual certification of disease free status, when achieved
- Certification for batches of accredited animals going to sales
- Advertising of herd details, if requested
The scheme
is conducted according to the guidelines of Cattle Health Certification Standards (UK) (CHeCS), a self-regulatory body set up by the cattle industry to ensure consistency between different schemes and herds.
These guidelines cover requirements for sampling and biosecurity.
Samples are typically taken by a private veterinary practitioner and submitted to VSD on the appropriate submission form.
Samples must be appropriately identified.
For each disease, herds may join the scheme at a number of different levels, depending on circumstances and status:
Monitoring programmes
Testing carried out on bulk tank milk samples, so only available to dairy herds.
- Monitoring gives a good assessment of the health status of the herd, and of changes in this status over time.
- Depending on results, herd owners may then choose to follow a program of control and eradication and finally accreditation of disease-free status.
- No requirements for biosecurity. If herds later progress to a higher level of control, they must then keep a set of biosecurity rules designed to prevent accidental introduction of the disease that they are trying to control (or from which they are already accredited free).

Screening and Eradication programmes
- These programmes aim to reduce the effects of the diseases within herds and in the longer term should help achieve freedom and accredited status.
- Herds must follow the biosecurity rules.
- Requires a test program that may include blood, milk or faeces samples depending on the disease and herd in question.
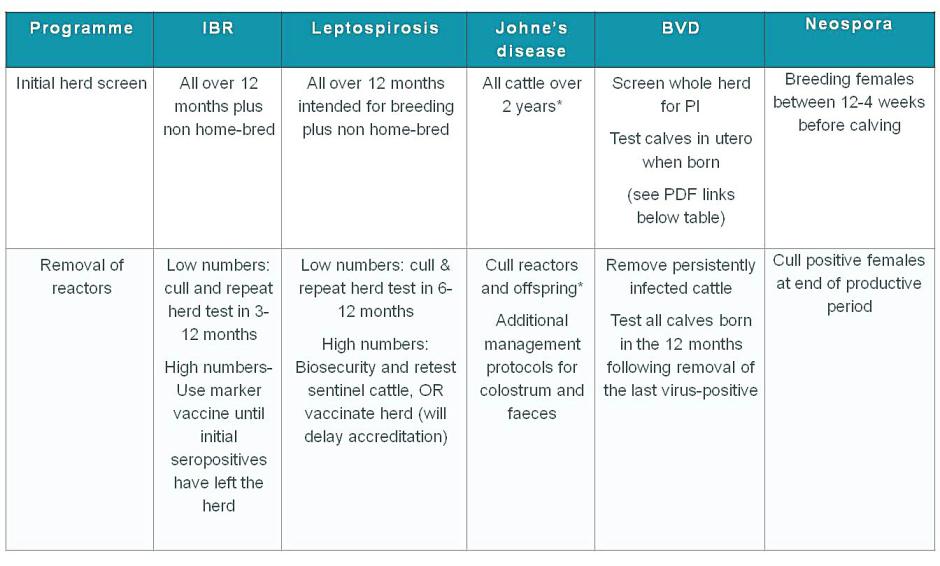
- For IBR, leptospirosis , Johne’s disease and neospora, an initial herd test (excluding younger stock) is carried out. If the results are all negative, this may be the first step toward accreditation (see below). If there are positive results, these animals may be removed from the herd. Where this is not possible (e.g. large numbers of positive animals), vaccination may be used for some of these diseases. If positive cattle are removed, then the initial herd test may then be repeated with a clear test then being the first step toward accreditation.
- The programme for BVD is similar, although a range of testing strategies are available.
Accreditation programmes
- Aim to demonstrate freedom from a given infection, to maintain that freedom and to certify the herd as free to allow the sale of accredited-free stock.
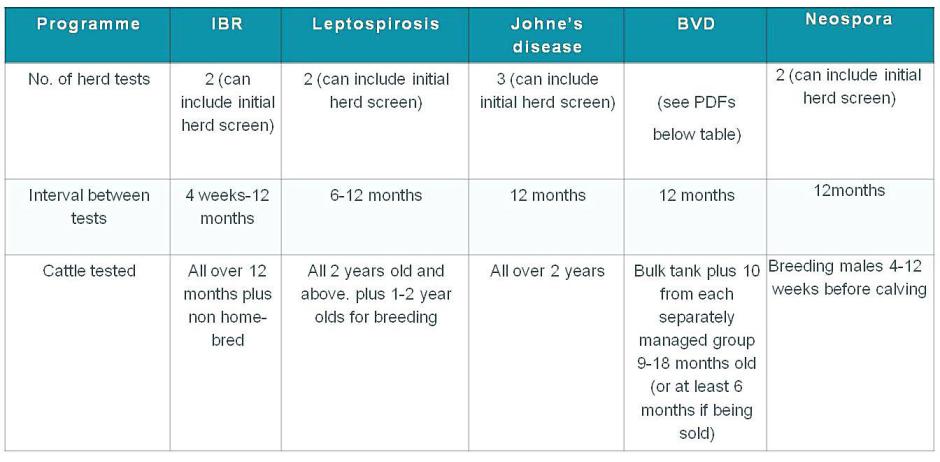
- For IBR, leptospirosis and Johne’s disease, an initial herd test (possibly excluding young stock) is carried out. If all results are negative, a second herd test is carried out some time later. If the results from this test are also negative, it may then be accredited for that disease. For Johne's disease where animals from non-accredited herds have passed through quarantine testing and been added to the herd they should not be sold as accredited animals until they have been in the herd for at least two clear annual tests.
- The programme for BVD is similar, although a range of testing strategies are available.
- To keep accredited status for a given disease, herds must continue to follow the CHeCS rules and to conduct regular sampling of selected cattle with negative results.
Testing to maintain accreditation

Vaccinated Monitored Free Programme
Sample sizes
Sample Size for IBR and Leptospirosis for annual tests in herds accredited free of infection

Sample Size for Neosporosis Snapshot Bleed

Vaccinated monitored free programme
- Only available for BVDV, and aims to control BVD through vaccination.
- This programme is aimed particularly at commercial herds selling stock for finishing.
- The absence of infection in young stock is used to demonstrate that the programme is effective.